Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data transmitted over an Internet connection in a given time, and it’s represented in the number of bits, kilobits, megabits, or gigabits that your connectivity can send in a second.
The terms Internet speed and bandwidth are often confused, but here is the difference. Speed refers to the rate at which data can be transmitted, while bandwidth is the capacity of that speed. Using an analogy, imagine a road; the speed will depend on the vehicle, and the bandwidth will depend on how many vehicles can travel simultaneously on the road for a given time.
How much bandwidth do I need?
Suppose several users and devices are connected to the Internet simultaneously. In that case, you will need a bandwidth that allows them to browse, connect to databases, make video calls, download, etc. correctly. These high-capacity digital activities require a certain amount of bandwidth to get a better experience by decreasing latency.
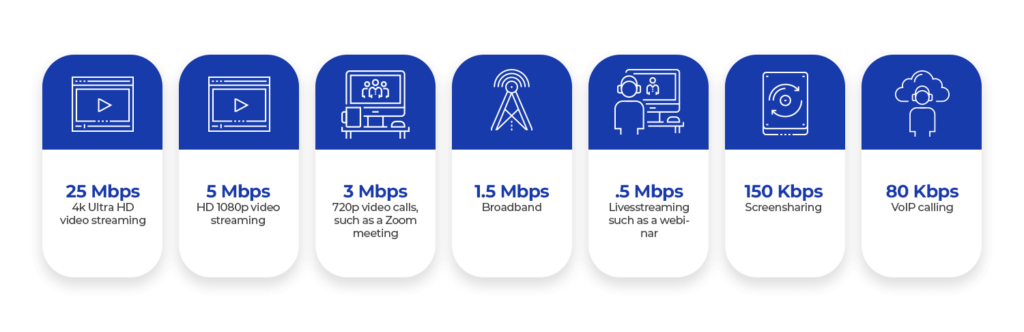
The Federal Communications Commission in the United States, FCC, made a report with the minimum bandwidth required for the most performed activities on the Internet. You can find a summary in the following image or see the full report by clicking here.
To understand what bandwidth you need for your Internet activities, we recommend following these steps:
- Determine which applications are going to be used and which are mission-critical.
- Define the bandwidth requirements of each application.
- Multiply the needs of each application by the number of users connected simultaneously.
- Add up all the bandwidth figures for the applications.
SD-WAN eases dedicated bandwidth capacity planning processes
Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) technology can provide additional capacity by balancing traffic across multiple WAN connections, DIA (Dedicated Internet Access), and mobile networks instead of a single connection.
To enhance your browsing experience with a better Internet connection, learn about the connectivity solutions Flō Networks has for your business.