Businesses invest significant resources in safeguarding the integrity of their data centers against various cyber threats, such as malware, spoofing, and phishing. However, it's important to note that they remain vulnerable to attacks that specifically target data in transit.
Types of encryption for data in transit
There are different types of encryption available, ranging from the physical layer to the higher application layers according to the Open Systems Interconnection Model (OSI model). Depending on the application and use cases, companies can choose different types of encryption that suit their specific needs.
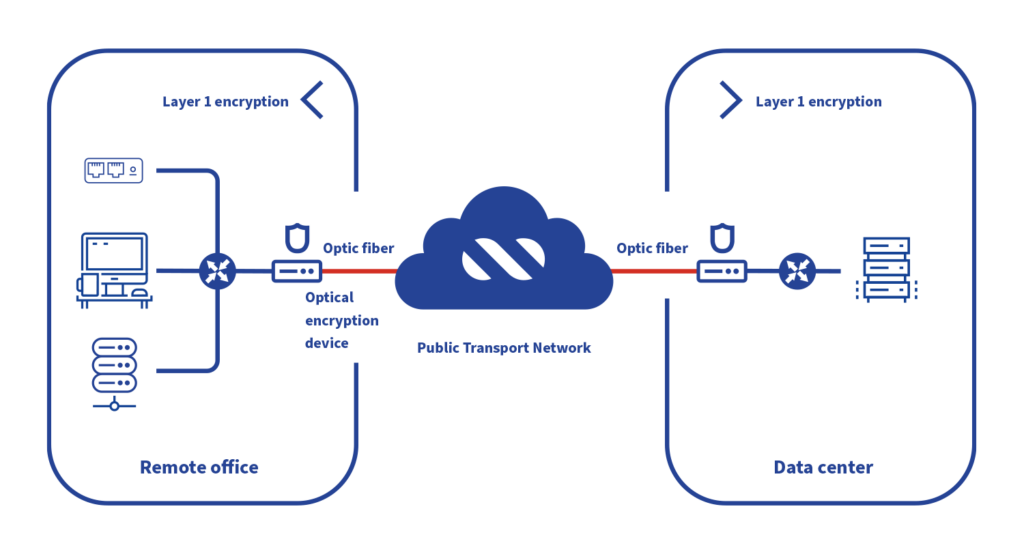
- Optical encryption, for instance, protects data at the physical layer (Layer 1) by transmitting protected signals over a fiber optic system. It is ideal for financial and healthcare applications that run over high-speed communication links (10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, 100 Gbps).
- On the other hand, Ethernet encryption at the link layer (Layer 2) can encrypt information using Media Access Control Security (MACsec) while using the Ethernet protocol, regardless of the transmission medium. HIPAA, PCI, and Sarbanes-Oxley already use MACsec as a valid mechanism for securing communications networks up to high capacities (<10G).
- Meanwhile, IPSec (Internet Security Protocol) is available as a framework and protocol for establishing secure tunnels (VPN) between sites connected by layer 3 or IP. IPSec is widely used in almost all industries to establish secure communications over the Internet in capacities that generally do not exceed 1G and several brands support standardized protocols.
- For encrypting traffic at higher application layers (Layer 4 to Layer 7), several protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS), were created to protect sessions in client-server environments.
Advantages of optical encryption
The choice of the encryption type depends on the environmental and security requirements of each business. For instance, when large volumes of information are transmitted in a scenario that is subject to strict regulations, optical encryption is imperative. In such circumstances, the benefits of optical encryption can be summarized into three key aspects.
Flexibility: As this encryption is provided over optical signals with total independence of the information transmitted in higher layers, it supports a wide variety of information formats, which makes this technology completely independent of the protocol chosen by the users.
Efficiency: Higher layer protocols use headers for information encryption, which reduces the capacity to send useful data for applications. This situation is more prominent for applications that use small packets of information, where the amount of information used to encrypt is significant to the amount of information used to transmit data that is valuable to the application. Conversely, encryption at the optical layer does not employ these headers, thereby allowing 100% of the available capacity to be utilized for sending valuable information, as is evident in the graph below.
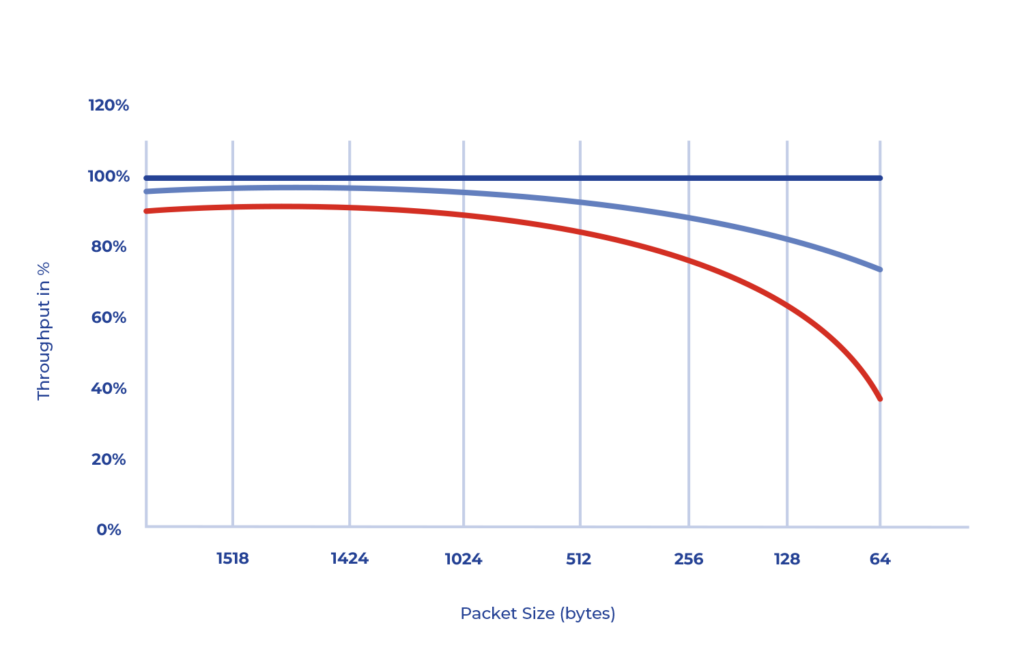
Delay: the delay generated during the encoding/decoding of optical signals is significantly lower, almost imperceptible, when compared to other encryption mechanisms at higher layers.
Advantages of Ethernet encryption
Ethernet encryption, like optical encryption, is well-suited for scenarios that require high-capacity information transmission with strict security standards. In addition, the use of the MACsec protocol for encryption at this layer provides the following advantages:
Transport independence: MACsec establishes secure data transfer between two devices regardless of intermediate devices or networks, as long as an Ethernet format is available at each end. In contrast, optical encryption requires OTN (Optical Transport Networking) to function.
Costs: Although the cost of layer 2 encryption using the MACsec protocol is higher than that of optical encryption given equivalent capabilities and equipment costs, it is still a cost-effective solution.
Efficiency: Layer 2 encryption services may have slightly longer delays compared to optical encryption, but they remain superior to higher-layer data-in-transit protection mechanisms in the environments described.
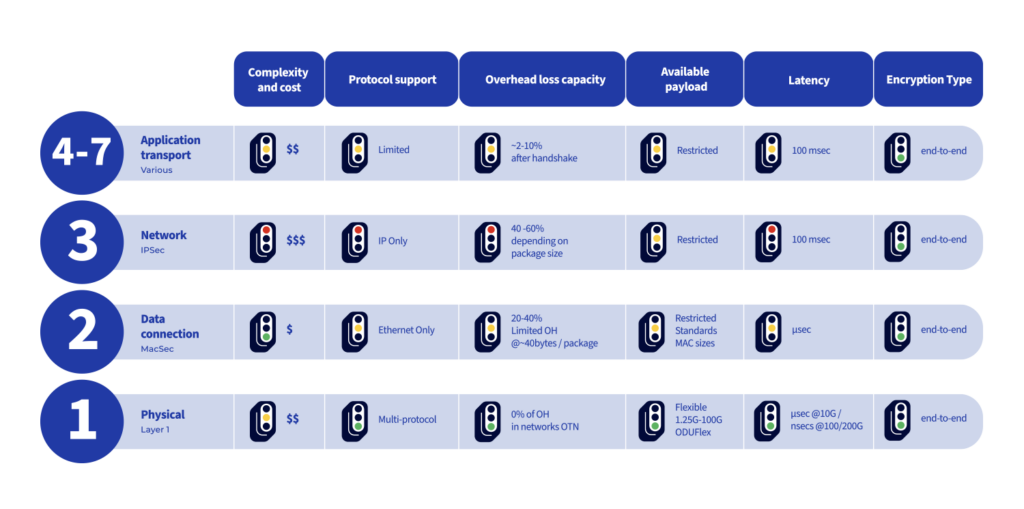
The table below shows the varying cost and quality of service variables that result from performing encryption at different layers:
What type of encryption is best for your company?
Determining the optimal encryption type for your company depends on several factors, such as environmental and security requirements. The question of which network layer is most suitable for securing data in transit has been the subject of debate. Some argue that sensitive data residing in the application layer makes it the most appropriate layer to secure, while others argue that data security should start at the physical layer, protecting protocol information involved in data movement. However, the answer to this question ultimately depends on the specific needs of each company.
At Flō Networks, we specialize in identifying and implementing the most suitable encryption solution for your business. With over 20 years of experience providing connectivity solutions and services using various encryption methods, we have a proven track record of success. Our unparalleled optical infrastructure (OTN) allows us to deploy encryption solutions in different service layers, and we have the technological alliances, processes, and trained resources to operate encryption services that meet the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS – Level 2) standards. Let us help you secure your data with the best encryption solution for your needs.

